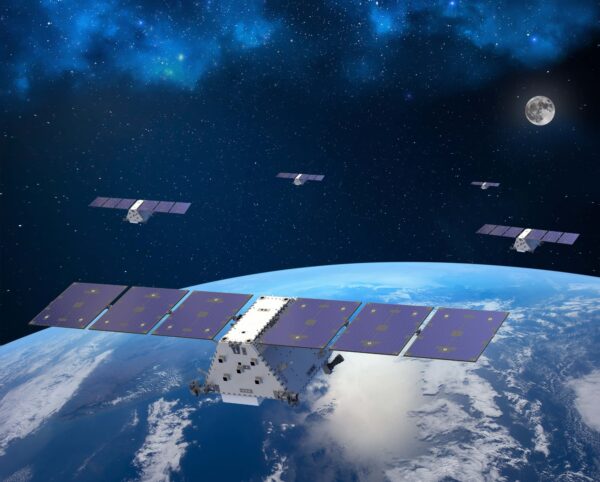
Lockheed Martin has announced that its satellite system update in space is ready to be released into space. These cubisats are designed to improve existing satellites, adding new capacities while extending the useful life and usefulness of satellites. Linuss cubesats are described as demonstration units.
Lockheed has developed two lm 50 12u cubsats called linuss; Each unit is, depending on the company, around the size of a toaster that contains four slices of bread. Both satellites are designed to demonstrate the use of cubisats, a small satellite type, as an effective way to update satellites that are already in space.
The mission is focusing on the updatable satellite shuttle platforms of LM 2100, the company revealed, and things will go off with the GPS IIIF 13 space vehicle 13. As of August 10, Lockheed said that its cubesat system enveloped environmental tests, Which means you are ready to launch at some point in 2021.
The company affirms that its Linuss satellites will be between the “more capable” cubsats sent to geosinctural orbit of the Earth. This launch will be used to demonstrate this update technology when validating “essential maneuver capabilities,” Lockheed explained this week.
Several technologies during this mission will be demonstrated, paving the way for future satellite services and updates. Lockheed is not alien to the launch of small satellites, according to the company, has deployed more than 150 of these small ships since the end of the 1990s.
The Micronedle patch with nanoparticles invests the baldness in a new studyA new study published by the details of the American Chemical Society promising research to revive baldness using nanoparticles. Medical technology, which uses microaguas as the delivery mechanism, addresses androgenic alopecia, the most common cause of masculine and female pattern baldness.
In the nucleus of androgen alopecia is the loss of cells that drive new hair formation, as well as the lack of a blood flow adequate to the hair follicles that deprive them with essential compounds for hair growth. Hair loss of this variety is permanent and, unfortunately, common treatments generally produce less than stellars.
A chemical element called Cerio has a promise as a solution for this problem; The researchers previously found that cerium-containing nanoparticles eliminate an overabundance of reactive oxygen species, which can accumulate in the scalp to cause early cell death.
The researchers behind the last study explored a micronedle patch as a way to deliver cerium nanoparticles beyond theouter layer of the skin and even the roots of deep hair. The microneedle patch was manufactured by combining nanoparticles with hyaluronic acid and pouring the mixture into a mold.
The patches were tested in mice that had bald points. The results showed that both traditional treatments and Microneedle patch could trigger the development of new blood vessels around the hair follicles. However, the patch offered faster results and reduced the number of oxidative stress compounds. In the same way, the patch can be used less frequently than other treatments while offering diameter, density and similar hair coverage.
The study involved mice, of course, and additional research would be necessary to explore the potential use of these nanoparticles in humans. However, researchers say that their findings indicate that Micronedele patches can be a viable form of reversing baldness in the future.